Deploy NFT Smart Contract (ERC721)
What are NFTs?
NFTs are individual tokens with valuable information stored in them. Because they hold a value primarily set by the market and demand, they can be bought and sold just like other physical types of art. NFTs’ immutable data stored on technologies like blockchain makes it easy to assign/validate its ownership and transfer tokens between two parties transparently without any intermediary.
NFT is a virtual digital asset that is typically unique and scarce similar to a Mona Lisa painting. An NFT is unique evidence of ownership of a virtual digital asset. You can read more about the use cases of NFTs like ‘NFT for Causes’ and ‘Private Club Memberships’ here. And smart contracts are one of the best use cases/innovations of blockchain technology. It is a virtual settlement between two parties enforced through a computer program (code) instead of a third party. You can find more on smart contracts and their deployment on Shardeum using Hardhat here, which would have similar coding as below since we will be using Hardhat for this documentation of deploying an NFT smart contract.
NFT Smart Contract Deployment Using Hardhat
Step 1 : Initialize Our Project
First, we’ll need to create a folder for our project. Navigate to your command line and type the following commands.
- Shell
mkdir shardeum-nft-dapp
cd shardeum-nft-dapp
Now that we’re inside our project folder, we’ll use ‘npm init’ to initialize the project. If you don’t have npm installed already, download from here Node.
- Shell
npm init
This command will create a package.json file. It doesn’t really matter how you answer the installation questions, here is how we did it for reference.
package name: (shardeum-nft-dapp)
version: (1.0.0)
description:
entry point: (index.js)
test command:
git repository:
keywords:
author:
license: (ISC)
About to write to G:shardeum-nft-dapppackage.json:
{
"name": "shardeum-nft-dapp",
"version": "1.0.0",
"description": "",
"main": "index.js",
"scripts": {
"test": "echo "Error: no test specified" && exit 1"
},
"author": "",
"license": "ISC"
}
Is this OK? (yes) yes
Step 2 : Download Hardhat
Hardhat is a development environment to compile, deploy, test, and debug your Ethereum software. It helps developers when building smart contracts and dApps locally before deploying to the live chain.
Inside our shardeum-nft-dapp project run:
- Shell
npm install --save-dev hardhat
Step 3 : Create Hardhat Project
Inside our shardeum-nft-dapp project run:
- Shell
npx hardhat
You should then see a welcome message and option to select what you want to do. Select “create an empty hardhat.config.js”:
G:shardeum-nft-dapp>npx hardhat
888 888 888 888 888
888 888 888 888 888
888 888 888 888 888
8888888888 8888b. 888d888 .d88888 88888b. 8888b. 888888
888 888 "88b 888P" d88" 888 888 "88b "88b 888
888 888 .d888888 888 888 888 888 888 .d888888 888
888 888 888 888 888 Y88b 888 888 888 888 888 Y88b.
888 888 "Y888888 888 "Y88888 888 888 "Y888888 "Y888
Welcome to Hardhat v2.9.5
? What do you want to do? ...
> Create a basic sample project
Create an advanced sample project
Create an advanced sample project that uses TypeScript
Create an empty hardhat.config.js
Quit
This will generate a hardhat.config.js file for us, which is where we’ll specify all of the set up for our project.
Step 4 : Project Folders
To keep our project organized, Hardhat creates two new folders. Navigate to the root directory of your shardeum-nft-dapp
- contracts/ is where we’ll keep our hello world smart contract code file
- scripts/ is where we’ll keep scripts to deploy and interact with our contract
Step 5 : Write Our Contract
Open up the shardeum-nft-dapp project in your favorite editor. Smart contracts are written in a language called Solidity which is what we will use to write our Domains.sol smart contract
- Navigate to the “contracts” folder and create a new file called Domains.sol
- Below is Domains smart contract from the nft.shardeum.us that we will be using for this tutorial. Copy and paste in the contents below into your Domains.sol file.
- Solidity
// SPDX-License-Identifier: MIT
pragma solidity 0.8.17;
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/token/ERC721/extensions/ERC721URIStorage.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Counters.sol";
import "@openzeppelin/contracts/utils/Base64.sol";
// import "hardhat/console.sol";
contract Domains is ERC721URIStorage {
error Unauthorized();
error AlreadyRegistered();
error InvalidName(string name);
using Counters for Counters.Counter;
Counters.Counter private _tokenIds;
string public tld;
mapping(string => address) public domains;
mapping(string => string) public records;
mapping(uint => string) public names;
address payable public owner;
string svgPartOne = '<svg xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg" width="270" height="270" fill="none"><path fill="url(#a)" d="M0 0h270v270H0z"/><defs><filter id="b" color-interpolation-filters="sRGB" filterUnits="userSpaceOnUse" height="270" width="270"><feDropShadow dx="0" dy="1" stdDeviation="2" flood-opacity=".225" width="200%" height="200%"/></filter></defs><svg x="15" y="15" width="120" height="108" viewBox="0 0 120 108" fill="none" xmlns="http://www.w3.org/2000/svg"><path d="M29.4358 77.2888L16.7213 100H103.279L90.5643 77.2888H29.4358Z" fill="white"/><path d="M60 22.7112L47.2856 0L4 77.2889H29.4358L60 22.7112Z" fill="white"/><path d="M90.5642 77.2889H116L72.7145 -3.05176e-05L60 22.7111L90.5642 77.2889Z" fill="white"/><path d="M60 73.3853C67.6037 73.3853 73.7677 67.0303 73.7677 59.1909C73.7677 51.3515 67.6037 44.9964 60 44.9964C52.3964 44.9964 46.2324 51.3515 46.2324 59.1909C46.2324 67.0303 52.3964 73.3853 60 73.3853Z" fill="white"/></svg><defs><linearGradient id="a" x1="0" y1="0" x2="270" y2="270" gradientUnits="userSpaceOnUse"><stop stop-color="#cb5eee"/><stop offset="1" stop-color="#0cd7e4" stop-opacity=".99"/></linearGradient></defs><text x="32.5" y="231" font-size="27" fill="#fff" filter="url(#b)" font-family="Plus Jakarta Sans,DejaVu Sans,Noto Color Emoji,Apple Color Emoji,sans-serif" font-weight="bold">';
string svgPartTwo = '</text></svg>';
constructor(string memory _tld) ERC721("Web3 user name NFT on shardeum | SHM", "Web3 User Name") payable {
owner = payable(msg.sender);
tld = _tld;
// console.log("%s name services deployed", _tld);
}
function price(string calldata name) public pure returns(uint){
uint len = StringUtils.strlen(name);
require(len > 2);
if(len == 3){
return 90 * 10**17;
}else if(len == 4){
return 50 * 10**17;
}else if(len == 5){
return 30 * 10**17;
}else{
return 10 * 10**17;
}
}
function registers(string calldata name) public payable {
// require(domains[name] == address(0));
if(domains[name] != address(0)) revert AlreadyRegistered();
if(!valid(name)) revert InvalidName(name);
uint _price = price(name);
require(msg.value >= _price, "not enough SHM paid");
string memory _name = string(abi.encodePacked(name, ".", tld));
// console.log("_name", _name);
string memory finalSvg = string(abi.encodePacked(svgPartOne, _name, svgPartTwo));
uint256 newRecordId = _tokenIds.current();
uint256 length = StringUtils.strlen(name);
string memory strLen = Strings.toString(length);
// console.log("Registering %s on the contract with tokenId %d", name, newRecordId);
string memory json = Base64.encode(
bytes(
string(
abi.encodePacked(
'{"name":"',
_name,
'","description":"Web3 user name NFT on shardeum | SHM","image":"data:image/svg+xml;base64,',
Base64.encode(bytes(finalSvg)),
'","length":"',
strLen,
'"}'
)
)
)
);
string memory finalTokenUri = string(abi.encodePacked("data:application/json;base64,", json));
// console.log("\n--------------------------------------------------------");
// console.log("Final tokenURI", finalTokenUri);
// console.log("--------------------------------------------------------\n");
_safeMint(msg.sender, newRecordId);
_setTokenURI(newRecordId, finalTokenUri);
domains[name] = msg.sender;
// console.log("%s has registered a domain", msg.sender);
names[newRecordId] = name;
_tokenIds.increment();
}
function getAddress(string calldata name) public view returns (address){
return domains[name];
}
function setRecord(string calldata name ,string calldata record) public {
// require(domains[name] == msg.sender);
if(msg.sender != domains[name]) revert Unauthorized();
records[name] = record;
}
function getRecord(string calldata name) public view returns(string memory){
return records[name];
}
modifier onlyOwner(){
require(isOwner());
_;
}
function isOwner() public view returns (bool){
return msg.sender == owner;
}
function withdraw() public onlyOwner{
uint amount = address(this).balance;
(bool success, ) = msg.sender.call{value: amount}("");
require(success, "failed to withdraw SHM");
}
function getAllNames() public view returns(string[] memory){
string[] memory allNames = new string[](_tokenIds.current());
for(uint i = 0; i < _tokenIds.current(); i++){
// console.log("iteration i names[i] ", names[i]);
// console.log("iteration i allNames[i] ", allNames[i]);
allNames[i] = names[i];
}
return allNames;
}
function valid(string calldata name) public pure returns(bool){
return StringUtils.strlen(name) >= 3 && StringUtils.strlen(name) <= 10;
}
}
library StringUtils { // Source: ENS contracts: //https://github.com/ensdomains/ens-contracts/blob/master/contracts/ethregistrar/StringUtils.sol
function strlen(string memory s) internal pure returns (uint256) {
uint256 len;
uint256 i = 0;
uint256 bytelength = bytes(s).length;
for (len = 0; i < bytelength; len++) {
bytes1 b = bytes(s)[i];
if (b < 0x80) {
i += 1;
} else if (b < 0xE0) {
i += 2;
} else if (b < 0xF0) {
i += 3;
} else if (b < 0xF8) {
i += 4;
} else if (b < 0xFC) {
i += 5;
} else {
i += 6;
}
}
return len;
}
}
This is the smart contract that creates Shardeum .shm Domains by calling registers function with your desired name.
We used OpenZeppelin Contracts that helps you to minimize risks by using battle-tested libraries of smart contracts for Ethereum and other blockchains. It includes the most used implementations of ERC standards.
- Shell
npm install @openzeppelin/contracts
Now that we have created smart contract, we need to deploy this smart contract to the Shardeum Sphinx
Step 6 : Add the Shardeum Network to Metamask/Claim Token
MetaMask allows users to store and manage account keys, broadcast transactions, send and receive Ethereum-based cryptocurrencies and tokens, and securely connect to decentralized applications through a compatible web browser or the mobile app’s built-in browser. Click here to install the MetaMask extension on your browser.
And follow these instructions to add Shardeum to MetaMask wallet and claim test 100 $SHM tokens from Sphinx faucet.
Step 7 : Connect MetaMask to Your Project
We’ve created a MetaMask wallet and written our smart contract, and now it’s time to connect these two!
Every transaction sent from your virtual wallet requires a signature using your unique private key. To provide our program with this permission, we can safely store our private key in an environment file.
First, install the dotenv package in your project directory:
- Shell
npm install dotenv --save
Note:
.env
- Your environment file must be named .env or it won’t be recognized as an environment file. Do not name it process.env or .env-custom or anything else.
Your .env should look like this:
SHARDEUM_RPC=https://sphinx.shardeum.org/
PRIVATE_KEY= Your_Metamask_Private_Key
To actually connect these to our code, we’ll reference these variables in our hardhat.config.js file
Step 8 : Install Ethers.js
Ethers.js is a library that makes it easier to interact and make requests to Ethereum by wrapping standard JSON-RPC methods with more user friendly methods.
Hardhat makes it super easy to integrate Plugins for additional tooling and extended functionality. We’ll be taking advantage of the Ethers plugin for contract deployment (Ethers.js has some super clean contract deployment methods).
In your project directory type:
- Shell
npm install --save-dev @nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers "ethers@^5.0.0"
npm install --save-dev @nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle 'ethereum-waffle@^3.0.0'
We’ll also require ethers in our hardhat.config.js in the next step.
Step 9 : Update hardhat.config.js
We’ve added several dependencies and plugins so far, now we need to update hardhat.config.js so that our project knows about all of them.
Update your hardhat.config.js to look like this:
- Javascript
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-waffle");
require("@nomiclabs/hardhat-ethers");
require("dotenv").config();
const SHARDEUM_RPC = process.env.SHARDEUM_RPC;
const privateKey = process.env.PRIVATE_KEY;
/**
* @type import('hardhat/config').HardhatUserConfig
*/
module.exports = {
defaultNetwork: "hardhat",
solidity: {
version: "0.8.10",
},
networks: {
shardeum: {
url: SHARDEUM_RPC,
accounts: [privateKey],
chainId: 8080,
}
},
};
Step 10 : Compile Our Contract
To make sure everything is working so far, let’s compile our contract. The compile task is one of the built-in hardhat tasks.
From the command line run:
- Shell
npx hardhat compile
If no errors, it will compile successfully.
Compiled 16 Solidity files successfully
Step 11 : Write Our Deploy Script
Now that our contract is written and our configuration file is good to go, it’s time to write our contract deploy script.
Navigate to the /scripts folder and create a new file called deploy.js, adding the following contents to it:
- Javascript
const hre = require("hardhat");
const main = async ()=>{
const domainContractFactory = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("Domains");
const domainContract = await domainContractFactory.deploy("shm")
await domainContract.deployed()
console.log("contract depolyed to : ", domainContract.address)
}
const runMain = async ()=>{
try {
await main()
process.exit(0);
} catch (error) {
console.log("error: ",error)
process.exit(1)
}
}
runMain();
Hardhat does an amazing job of explaining what each line of these codes does in their contracts tutorial. We’ve adopted their explanations here.
const domainContractFactory = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("Domains");
A ContractFactory in ethers.js is an abstraction used to deploy new smart contracts, so Disperse here is a factory for instances of our Disperse contract. When using the hardhat-ethers plugin ContractFactory and Contract, instances are connected to the first signer (owner) by default.
await domainContract.deployed()
Calling deploy() on a ContractFactory will start the deployment, and return a Promise that resolves to a Contract object. This is the object that has a method for each of our smart contract functions.
Step 12 : Deploy Our Contract Local Hardhat Environment
Before we deploy our smart contract to Shardeum network, lets test this once in local hardhat environment to check what a generated Shardeum NFT looks like:
create a test-deploy.js file in scripts/ and copy paste the below code:
- Javascript
const hre = require("hardhat");
const main = async ()=>{
// const [owner, superCoder] = await hre.ethers.getSigners();
const domainContractFactory = await hre.ethers.getContractFactory("Domains");
const domainContract = await domainContractFactory.deploy("shm")
await domainContract.deployed()
console.log("contract depolyed to : ", domainContract.address)
let setDR = await domainContract.registers("contract",{value: hre.ethers.utils.parseEther("1")});
await setDR.wait();
console.log("Minted domain contract.shm")
const addr = await domainContract.getAddress("contract");
console.log("owner of contract domain : ", addr);
}
const runMain = async ()=>{
try {
await main()
process.exit(0);
} catch (error) {
console.log("error: ",error)
process.exit(1)
}
}
runMain();
Run this command in command prompt:
- Shell
node scripts/test-deploy.js
You should then see something like this:
G:\shardeum-nft-dapp>node scripts/deploy-domains.jsshm name services deployed
contract depolyed to : 0x5FbDB2315678afecb367f032d93F642f64180aa3
_name contract.shm
Registering contract on the contract with tokenId 0
--------------------------------------------------------
Final tokenURI data:application/json;base64,eyJuYW1lIjoiY29udHJhY3Quc2htIiwiZGVzY3JpcHRpb24iOiJXZWIzIHVzZXIgbmFtZSBORlQgb24gc2hhcmRldW0gfCBTSE0iLCJpbWFnZSI6ImRhdGE6aW1hZ2Uvc3ZnK3htbDtiYXNlNjQsUEhOMlp5QjRiV3h1Y3owaWFIUjBjRG92TDNkM2R5NTNNeTV2Y21jdk1qQXdNQzl6ZG1jaUlIZHBaSFJvUFNJeU56QWlJR2hsYVdkb2REMGlNamN3SWlCbWFXeHNQU0p1YjI1bElqNDhjR0YwYUNCbWFXeHNQU0oxY213b0kyRXBJaUJrUFNKTk1DQXdhREkzTUhZeU56QklNSG9pTHo0OFpHVm1jejQ4Wm1sc2RHVnlJR2xrUFNKaUlpQmpiMnh2Y2kxcGJuUmxjbkJ2YkdGMGFXOXVMV1pwYkhSbGNuTTlJbk5TUjBJaUlHWnBiSFJsY2xWdWFYUnpQU0oxYzJWeVUzQmhZMlZQYmxWelpTSWdhR1ZwWjJoMFBTSXlOekFpSUhkcFpIUm9QU0l5TnpBaVBqeG1aVVJ5YjNCVGFHRmtiM2NnWkhnOUlqQWlJR1I1UFNJeElpQnpkR1JFWlhacFlYUnBiMjQ5SWpJaUlHWnNiMjlrTFc5d1lXTnBkSGs5SWk0eU1qVWlJSGRwWkhSb1BTSXlNREFsSWlCb1pXbG5hSFE5SWpJd01DVWlMejQ4TDJacGJIUmxjajQ4TDJSbFpuTStQSE4yWnlCNFBTSXhOU0lnZVQwaU1UVWlJSGRwWkhSb1BTSXhNakFpSUdobGFXZG9kRDBpTVRBNElpQjJhV1YzUW05NFBTSXdJREFnTVRJd0lERXdPQ0lnWm1sc2JEMGlibTl1WlNJZ2VHMXNibk05SW1oMGRIQTZMeTkzZDNjdWR6TXViM0puTHpJd01EQXZjM1puSWo0OGNHRjBhQ0JrUFNKTk1qa3VORE0xT0NBM055NHlPRGc0VERFMkxqY3lNVE1nTVRBd1NERXdNeTR5TnpsTU9UQXVOVFkwTXlBM055NHlPRGc0U0RJNUxqUXpOVGhhSWlCbWFXeHNQU0ozYUdsMFpTSXZQanh3WVhSb0lHUTlJazAyTUNBeU1pNDNNVEV5VERRM0xqSTROVFlnTUV3MElEYzNMakk0T0RsSU1qa3VORE0xT0V3Mk1DQXlNaTQzTVRFeVdpSWdabWxzYkQwaWQyaHBkR1VpTHo0OGNHRjBhQ0JrUFNKTk9UQXVOVFkwTWlBM055NHlPRGc1U0RFeE5rdzNNaTQzTVRRMUlDMHpMakExTVRjMlpTMHdOVXcyTUNBeU1pNDNNVEV4VERrd0xqVTJORElnTnpjdU1qZzRPVm9pSUdacGJHdzlJbmRvYVhSbElpOCtQSEJoZEdnZ1pEMGlUVFl3SURjekxqTTROVE5ETmpjdU5qQXpOeUEzTXk0ek9EVXpJRGN6TGpjMk56Y2dOamN1TURNd015QTNNeTQzTmpjM0lEVTVMakU1TURsRE56TXVOelkzTnlBMU1TNHpOVEUxSURZM0xqWXdNemNnTkRRdU9UazJOQ0EyTUNBME5DNDVPVFkwUXpVeUxqTTVOalFnTkRRdU9UazJOQ0EwTmk0eU16STBJRFV4TGpNMU1UVWdORFl1TWpNeU5DQTFPUzR4T1RBNVF6UTJMakl6TWpRZ05qY3VNRE13TXlBMU1pNHpPVFkwSURjekxqTTROVE1nTmpBZ056TXVNemcxTTFvaUlHWnBiR3c5SW5kb2FYUmxJaTgrUEM5emRtYytQR1JsWm5NK1BHeHBibVZoY2tkeVlXUnBaVzUwSUdsa1BTSmhJaUI0TVQwaU1DSWdlVEU5SWpBaUlIZ3lQU0l5TnpBaUlIa3lQU0l5TnpBaUlHZHlZV1JwWlc1MFZXNXBkSE05SW5WelpYSlRjR0ZqWlU5dVZYTmxJajQ4YzNSdmNDQnpkRzl3TFdOdmJHOXlQU0lqWTJJMVpXVmxJaTgrUEhOMGIzQWdiMlptYzJWMFBTSXhJaUJ6ZEc5d0xXTnZiRzl5UFNJak1HTmtOMlUwSWlCemRHOXdMVzl3WVdOcGRIazlJaTQ1T1NJdlBqd3ZiR2x1WldGeVIzSmhaR2xsYm5RK1BDOWtaV1p6UGp4MFpYaDBJSGc5SWpNeUxqVWlJSGs5SWpJek1TSWdabTl1ZEMxemFYcGxQU0l5TnlJZ1ptbHNiRDBpSTJabVppSWdabWxzZEdWeVBTSjFjbXdvSTJJcElpQm1iMjUwTFdaaGJXbHNlVDBpVUd4MWN5QktZV3RoY25SaElGTmhibk1zUkdWcVlWWjFJRk5oYm5Nc1RtOTBieUJEYjJ4dmNpQkZiVzlxYVN4QmNIQnNaU0JEYjJ4dmNpQkZiVzlxYVN4ellXNXpMWE5sY21sbUlpQm1iMjUwTFhkbGFXZG9kRDBpWW05c1pDSStZMjl1ZEhKaFkzUXVjMmh0UEM5MFpYaDBQand2YzNablBnPT0iLCJsZW5ndGgiOiI4In0=
--------------------------------------------------------
0xf39fd6e51aad88f6f4ce6ab8827279cfffb92266 has registered a domain
Minted domain contract.shm
owner of contract domain : 0xf39Fd6e51aad88F6F4ce6aB8827279cffFb92266
Copy the Final tokenURI and paste in browser new tab which will look like this:
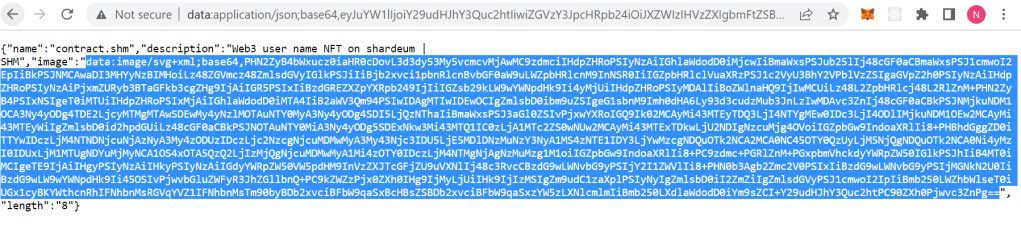
Now copy the data as selection shown above from the json and paste in new browser tab. This is how it may appear:
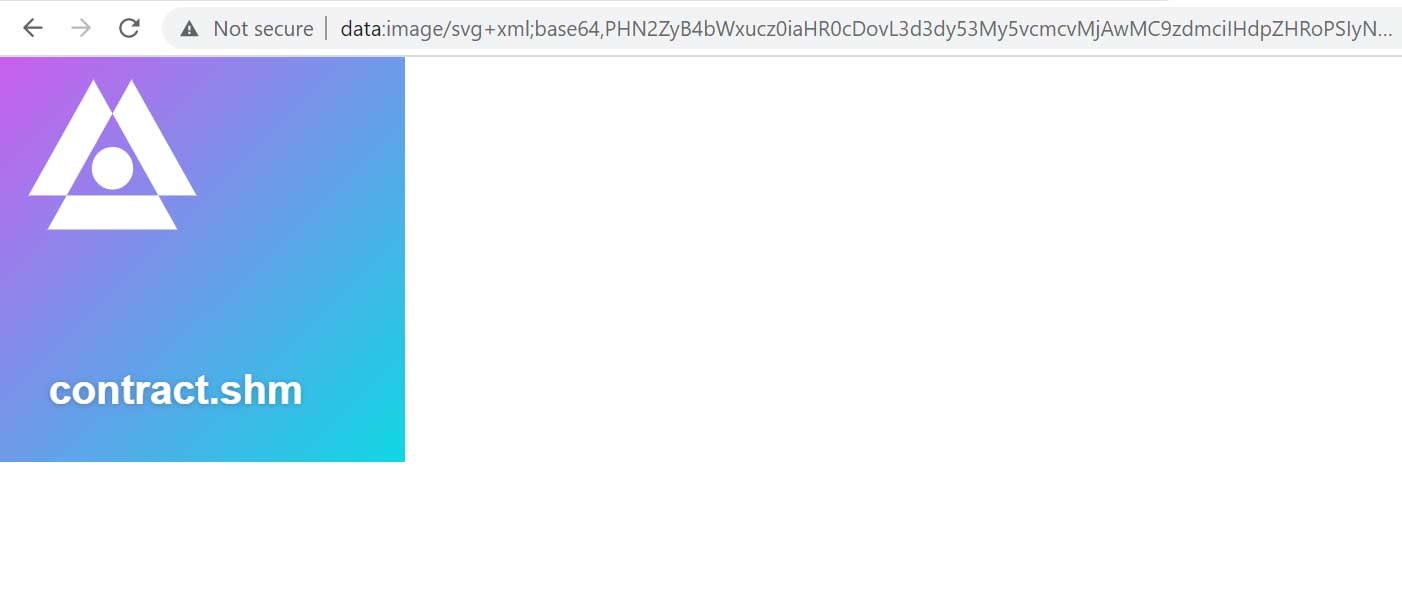
Step 13 : Deploy to Shardeum Sphinx testnet
In next line we are executing *(step 11) to deploy to Shardeum Network.
- Shell
npx hardhat run scripts/deploy.js --network shardeum
If we go to the Shardeum explorer and search for our contract address we should able to see that it has been deployed successfully.
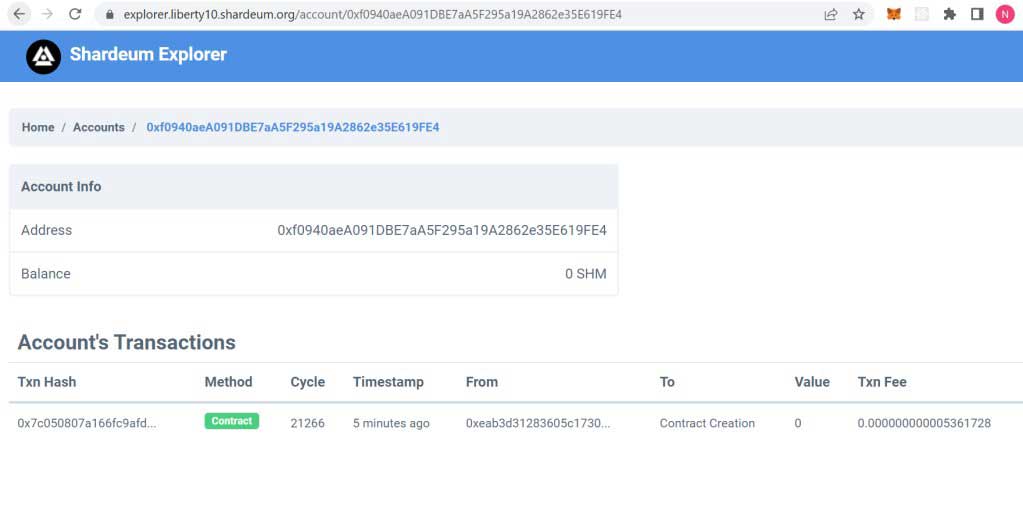
Click on Transaction hash to see the full details of contract creation:
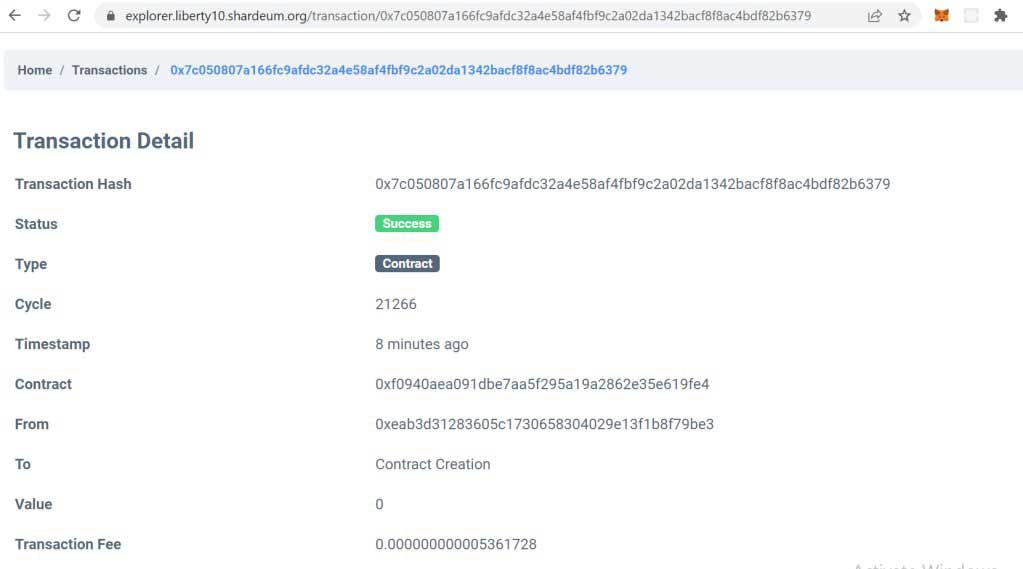
Congrats! You just deployed an NFT smart contract to the Shardeum Sphinx.